Powered Industrial Truck Types: Powered industrial trucks, commonly called forklifts or lift trucks, are used in many industries, primarily to move materials. They can be used to move, raise, lower, or remove large objects or a number of smaller objects on pallets or in boxes, crates, or other containers.

Class IV: Internal Combustion Engine Trucks (Solid/Cushion Tires) Class V: Internal Combustion Engine Trucks (Pneumatic Tires) Class VI: Electric and Internal Combustion Engine Tractors. Class VII: Rough Terrain Forklift Trucks. Class I: Electric Motor Rider Trucks. Electric Motor Rider Trucks. These forklifts can be equipped with either cushion or pneumatic tires. Managing lift trucks Key messages. Lift trucks are particularly dangerous in the workplace. On average, lift trucks are involved in about a quarter of all workplace transport accidents. Accidents involving lift trucks are often due to poor supervision and a lack of training. Safe working with lift trucks.
Contents
- 1 Types of powered industrial truck
Types of powered industrial truck
Forklifts and their many cousins in what OSHA lumps together as “powered industrial trucks” are among the most common vehicles on worksites – so common that it’s easy to take these workhorses for granted.
The number one rule is that anybody who uses a forklift must receive formal classroom training and hands-on training in its use and safety procedures.
The term forklift truck is a fairly broad term that can be used for a number of different vehicles. When people think of forklifts, they usually imagine the small vehicle with two forks on the front that’s used for lifting pallets. However, forklift trucks come in a number of different sizes and models.
With so many forklift types to choose from it can be difficult to find the forklift perfect for your environment. Choosing the wrong forklift can waste time, money, and effort. Let’s take a look at some of the most popular forklift classifications. (Powered Industrial Truck Types)
Electric Motor Rider Trucks
Class 1 electric motor rider trucks:
They are ideal for applications where air quality and fuel fumes are a concern. Most class one forklifts are used indoors with cushion tires designed for use on smooth floors. They can also be outfitted with pneumatic tires and used in dry, outdoor applications.
Electric Motor Narrow Aisle Trucks
class 2 electric motor narrow aisle trucks:
Operations that need to maximize their storage space use narrow-aisle material handling equipment such as reach trucks and order pickers to handle pallets and move inventory. These class two lift trucks need minimal space to operate and are powered by an electric motor.
Electric hand trucks
class 3 electric motor hand truck:
These are hand-controlled forklifts, meaning the operator is in front of the truck and controls the lift through a steering tiller. All controls are mounted on the top of the tiller, and the operator moves the tiller from side to side to steer the truck. These vehicles are battery-powered, and the smaller capacity units use industrial batteries.
Internal Combustion Engine Trucks
class 4 Internal Combustion Engine Trucks: (Solid/Cushion Tires)
These forklifts are used inside on smooth dry floors for transporting palletized loads to and from the loading dock and the storage area. The cushion-tired forklifts are lower to the ground than forklift trucks with pneumatic tires. Because of that, these forklift trucks can be useful in low-clearance applications.
Internal Combustion Engine Trucks
class 5 Internal Combustion Engine Trucks: (Pneumatic Tires)
These trucks are most commonly seen in warehouses. They can be used either inside or outside for virtually any type of application. Because of the large capacity range of this series of a lift trucks, they can be found handling small single pallet loads to loaded 40-foot containers.
The cushion-tired forklifts are lower to the ground than forklift trucks with pneumatic tires. Because of that, these forklift trucks can be useful in low-clearance applications.
Internal Combustion Engine Tractors
class 6 Internal Combustion Engine Tractors:
An internal combustion (IC) engine on a forklift works much like the engine on your personal car or truck and uses fuel to run. In the case of a forklift for sale or rent, this fuel is usually gasoline, diesel, liquefied petroleum gas, or compressed natural gas. The internal combustion engine is one of the most common types of engines in industrial equipment such as forklifts and with good reason.
Rough Terrain Forklift Trucks
class 7 Rough Terrain Forklift Trucks:
Rough terrain forklift is a generic term used to describe forklifts typically intended for use on unimproved natural terrain and disturbed terrain construction sites. However, the term “rough terrain” does not imply that the forklift can be safely operated on every conceivable type of terrain. Rough terrain forklifts have inflatable tires with thicker treads which allows it to gain stability on uneven surfaces.
Powered industrial truck training
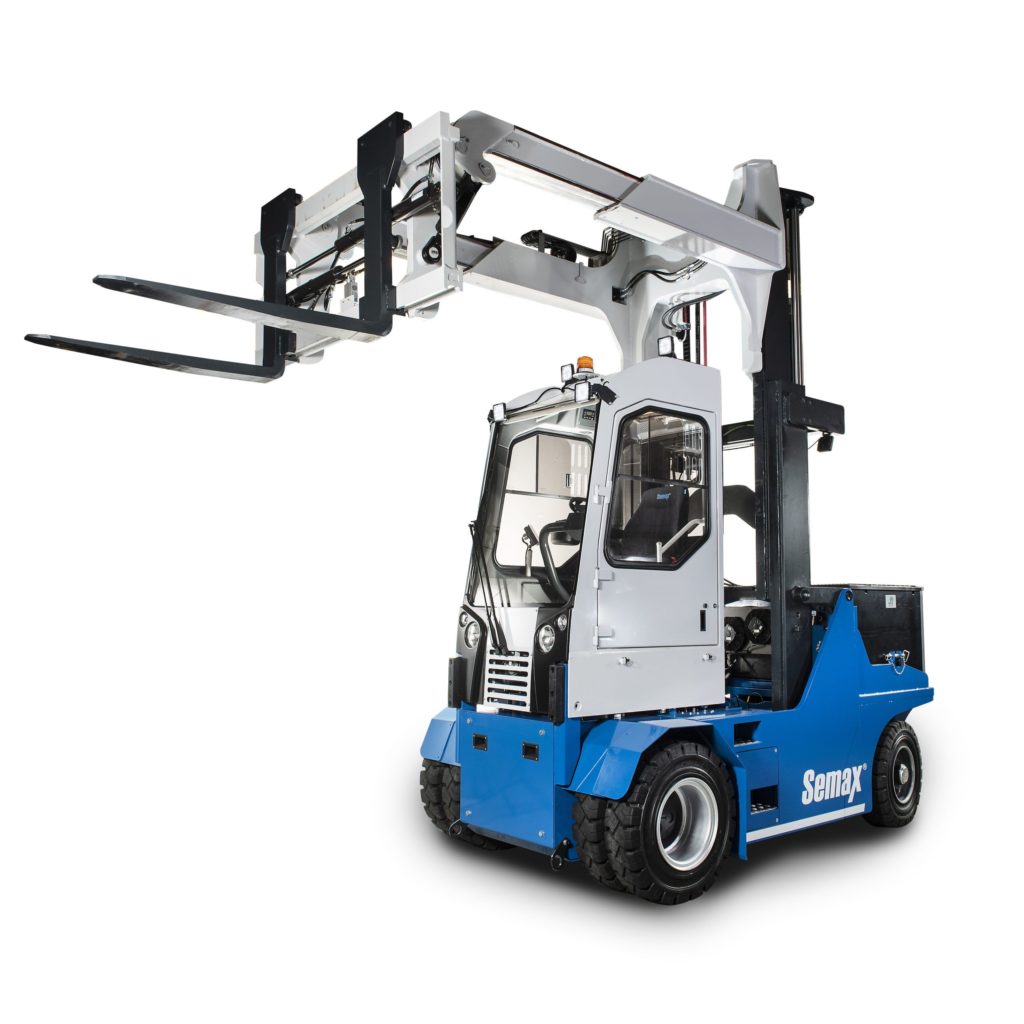

Powered Industrial Truck Types – Powered industrial truck training:
Although a typical forklift has four wheels and a steering column, it’s not at all like driving a car or truck. First, forklifts usually weigh at least twice as much. The seat tends to be elevated, creating a higher center of gravity that is less forgiving when it comes to tipping over.
They’ll turn on a dime, but the back end has a wider swing than other types of vehicles. Wheelbases tend to be even narrower than what you’ll find on a Mini Cooper. Turn too sharply while going quickly, or carry the load just a little too high, and there’s a good chance you’ll be on your side with a damaged load.
Training must cover inspection, the operation of the vehicle, proper loading and movement, safety precautions when operating around other people, and emergency procedures.
Once a worker has been trained on a particular type of equipment, he or she should be able to operate other makes and models of similar types with a brief orientation. However, just because an employee is trained for a forklift doesn’t mean he or she is ready to operate other types of powered equipment. If you’re in doubt, err on the side of extra training.
The most read
Stand-up Forklift
Stand-up forklifts (also known as stand-on and electric riders) are designed for applications where the operator must get on and off the lift truck frequently. They are more maneuverable and need less space to operate than sit-down forklifts.
Forklift rules and regulations
FORKLIFT SAFETY: forklift loader rules, guidelines and regulations, forklift rules and regulations, fork truck safety, forklift training license.
When buying or renting a lift truck, there are lots of factors to consider about the different types of forklifts and their uses. The first thing to think about is whether you operate indoors or outdoors, as each environment has unique needs. The next thing to consider is any restrictions you have, such as aisle widths or clearance heights. Finally, you need to think of the weight and height capacity you need and choose the right model accordingly.
Though there are dozens of different kinds of forklifts and models, knowing the broad categories of each type of forklift and their applications can help you narrow down your options. This guide to the different kinds of forklifts and their uses can help you determine which lift truck you need to improve your operations.

1. Warehouse Forklifts
Warehouse forklift is a general term to describe common lift trucks used indoors. Though there are many different types of forklifts for warehouse settings, what they have in common is they’re all lift trucks designed for efficient, safe and healthy indoor use. To operate in the warehouse, forklifts need specific qualities that make them the best option possible for their application. Some of the ideal features to look for in a warehouse forklift include:
- Clean energy: Warehouse forklifts must be powered by a clean energy source that doesn’t emit harmful fumes when operated indoors. With so many workers in confined spaces, it’s critical for health and safety standards that warehouse forklifts are powered by electrical energy sources, rather than diesel or gas-powered lifts.
- Turning radius:Indoor forklifts also need to have a tight turning radius, allowing them to easily navigate the narrow spaces found in warehouses. Indoor forklifts have a small design, and some can even turn around in their own footprint, making them ideal for narrow aisles.
- Lift capacity: In warehouses that stock and store a variety of goods, you need a forklift that has a larger weight capacity to be able to manage whatever goods you receive. Some warehouse forklifts have capacities up to 20,000 pounds, depending on the design. Always ensure you use a forklift than can comfortably handle your largest loads.
Despite the fact that all warehouses share a relatively common purpose, warehouse operators differ widely in what they need from their forklifts. That’s why a single warehouse operation may employ multiple different types of forklifts for various operational tasks. They may have some with lower reach and weight capacities, and others with taller reaches and larger weight capacities.
2. Electric Forklifts
Electric forklifts are warehouse forklifts powered by electricity from a battery rather than by diesel, gas or propane. They emit zero emissions, making them an eco-friendly choice for warehouses looking to meet specific sustainability goals. Because electric forklifts are battery powered, they are quieter than fuel-powered models. This reduced noise makes them ideally suited for the indoors where protecting worker hearing and improving communications is essential.
Electric forklifts can be either three-wheel or four-wheel machines, with the three-wheel configuration being more maneuverable than the four-wheel. Besides their indoor suitability, electric lift trucks are also capable of safely lifting, loading and unloading heavy loads with capacities ranging between 5,000 pounds and 20,000 pounds, depending on the model.
Holt of California is proud to offer the following brands of electric forklifts:
3. Counterbalance Forklifts
Counterbalance forklifts are considered the most common forklift in warehousing and manufacturing, and they’re usually the type that comes to mind when discussing different types of forklifts. Counterbalanced forklifts, also known as Class I forklifts according to OSHA, are electric-powered warehouse and industrial lift trucks that usually have a lower weight capacity between 3,000 pounds and 12,000 pounds. While OSHA defines this class as strictly electric, counterbalance forklifts also come in diesel- and propane-powered options.
Recognizable by their two front forks, counterbalance forklifts earn their name because the front load’s weight is balanced out by the equipment's weight in the rear. This offset ensures the forklift is able to maintain stability as it lifts loads to its capacity. While counterbalance forklifts are generally operated from a seated position, stand-up models do exist. The benefit of the stand-up option is that it’s more compact, making it more maneuverable. Because the operator is standing up, they can also benefit from improved visibility in all directions, potentially making the equipment safer to operate.
Counterbalance forklifts come in four-wheel and three-wheel models, with the three-wheel option being highly desirable in narrow warehouses due to its superior maneuverability. Three-wheel forklifts are generally recommended for indoor uses where there is smooth, even ground. They can also be used outdoors in building supply yards or other applications where there’s flat asphalt or concrete. Because three-wheel counterbalance forklifts are smaller, they generally have a smaller load capacity than their 4-wheeled counterparts. The typical load capacity for a three-wheel counterbalance forklift is around 5,000 pounds.
At Holt of California, you’ll find a range of counterbalance forklifts available, including Mitsubishi’s line of three- and four-wheel counterbalance forklifts in small and mid sizes.
4. Narrow Aisle Forklifts
Narrow aisle forklifts, also known to OSHA as Class II forklifts, are electric forklifts designed to be operated in narrow aisles and tight indoor spaces. Though they are compact, narrow aisle forklifts are also sturdy, safe and versatile in loading and lifting a variety of goods. Generally, warehouse operators and employees rely on narrow aisle forklifts for tasks like picking and stocking inventory.
Because of the superior maneuverability of narrow aisle forklifts, many busy, full and growing warehouses opt for this forklift type as their staple lift equipment. These forklifts are also a good investment if you plan on adding more racking and inventory over time. As warehouse space becomes a more precious commodity, warehouse managers need to use the most efficient tools at their disposal to increase productivity and reduce operating costs. Narrow aisle forklifts are one of the reliable solutions to achieve these goals.
Narrow aisle forklifts are smaller, simpler machines than larger industrial lift trucks. Their maintenance requirements are also lower, helping managers save money and preserve their investment. For warehouse managers wanting to save space and opt for the narrow aisle forklift, there are a few types of lift trucks for narrow aisles, including side loaders, cherry pickers — also known as order pickers — and reach trucks:
Side Loaders
Side loaders, also known as industrial side loaders, are a kind of indoor warehouse forklift typically used in manufacturing or wherever large, heavy items are being handled. Side loaders are operated from a side-facing compartment and move in a sideways fashion down the aisles with the operator facing the racks rather than down the aisle. As opposed to traditional forward-driving forklifts, side loaders save space by loading and unloading from the side without having to turn and face the rack in tight spaces.
Because side loaders run alongside racking systems, it makes them ideal as one of the best types of forklifts used in warehouses where long goods are being stores, such as timber or piping, which will only fit lengthwise down an aisle.
Side loaders come in two models: enclosed cabs and stand-up. Stand-up side loaders are commonly thought of as types of forklifts in warehouses, whereas enclosed cab side loaders are suitable for outdoor use. Some variations of side loaders have the ability to turn the wheels 90 degrees so the goods can be transported in any direction once out of the aisle. Depending on the model, some side loaders can obtain lifts of up to 30 feet.
Order Pickers
Not all types of industrial lift trucks have the strict duty of lifting materials or pallets. Certain types of lift trucks are designed to lift personnel. Order pickers, also known as cherry pickers, are types of forklifts used in construction, warehousing, installations and other applications to help technicians and workers reach up high. In warehouses, in particular, shelving racks can reach over 30 feet. When workers need to access inventory on the top shelves, they need a safe, controlled solution like order pickers to hand-pick goods safely.
Order pickers are typically electric-powered personnel lifts with a driver platform that extends upward. The benefit of this kind of forklift is that it allows the worker to lift up or retrieve only a few specific items at a time. Without an order picker lift truck, a warehouse worker would need to use a forklift to reach up and retrieve an entire load, such as a container, bring it down and then sort through it to find what they need. Order pickers save time by allowing a worker direct access to top-shelf goods. Because they’re meant for lifting to high shelves, order pickers are designed to fit in narrow aisles between shelving.
Order picker lift trucks from Holt of California come in various sizes and capacities — from small- to mid- to high-level reaches ranging from 9 feet to 30 feet with a load capacity up to 3,000 pounds.
Reach Trucks
While standard types of forklifts have forks that lift up and down only, reach trucks have forks that extend forward and back. Reach truck applications are typically for larger warehouses where vertical space is optimized. In order to reach significant heights, you need a reach truck that fits in the narrow aisles and reaches far enough. A reach truck provides this ability safely. Thanks to its stabilizer legs, reach trucks are sturdy and keep their balance without a rear counterbalance weight.
Types Of Lift Trucks
The benefit of having forks that reach ahead is that operators can extend the forks into the racking and retrieve loads, rather than relying on forks extending from the operator compartment. Some reach trucks are designed for their forks to extend twice as far as a standard forklift, meaning you can load two pallets at once.
Many trusted manufacturers supply reach trucks for warehouses with high racking setups. Here are some of the brands of reach truck models available from Holt of California:
5. Walkie Stacker
A walkie stacker is a simpler lift truck where the operator walks behind the truck. Walkie stackers are designed for warehouses because they are compact and can be easily maneuvered down narrow aisles. Walkie stackers are equipped with a motor, meaning the operator can move them backward and forward with basic controls.
The operator positions the forks of the walkie directly under the load, and the motorized lift raises the load effortlessly. Walkies are often seen as more efficient alternatives to hand pallet trucks because they lift heavier loads than manual versions. Despite their motorized lift mechanism, walkies are generally reserved for smaller-capacity loads since they’re built on a small frame and small wheels.
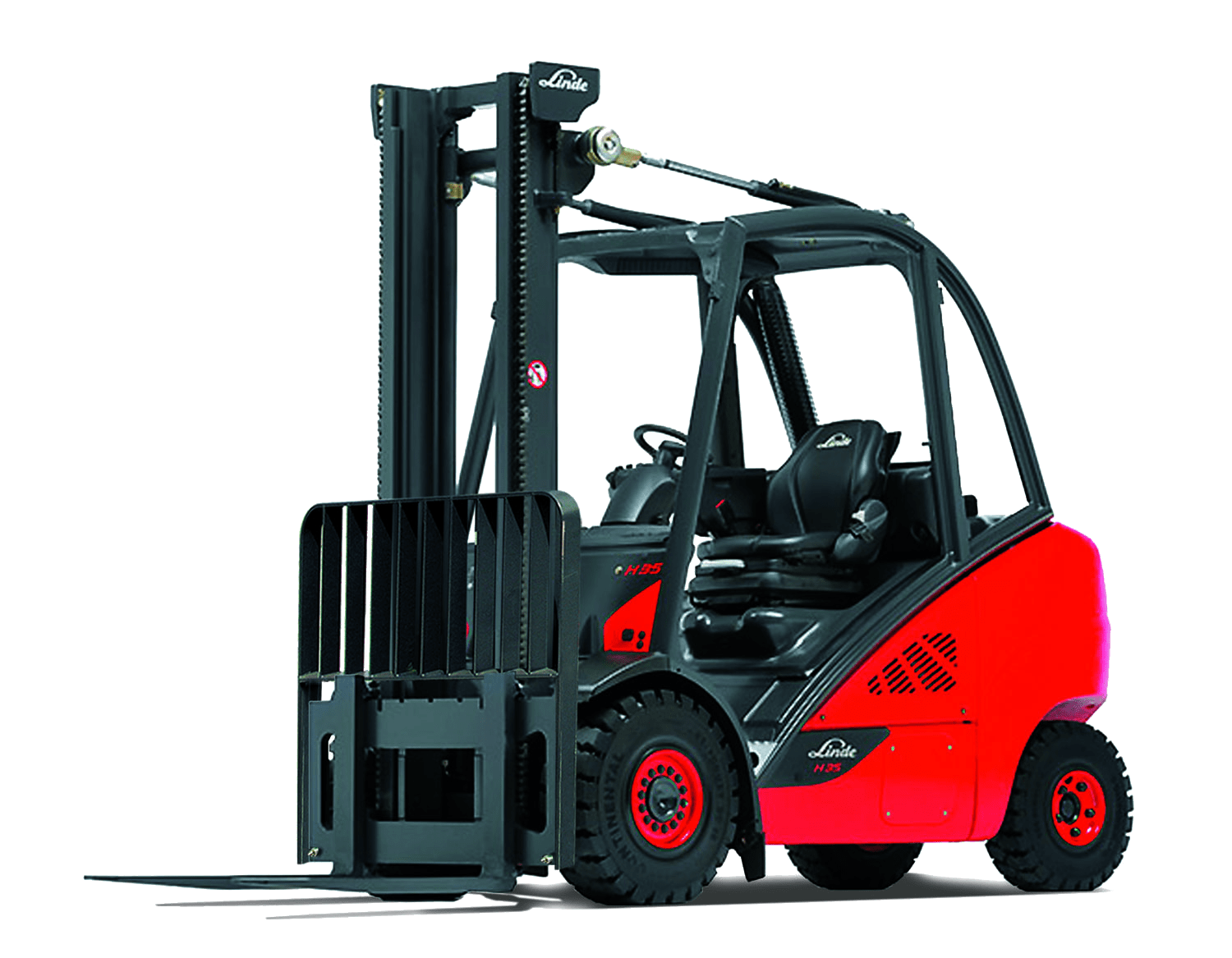

Some models have front legs to help distribute the weight, while others have legs on either side to help stabilize the load. Some models have no operator platform, while others do. Certain advanced models even offer the ability to adjust the stabilizer legs to accommodate different load sizes and aisle widths.
Since walkies aren’t as complex as other fully motorized warehouse forklifts, they’re often seen as a great compromise between manual pallet jacks and standard forklifts, which can be a significant investment. Walkies give you the efficiency of motorized lift capabilities at an economical price. Holt of California supplies seven different models of walkie stacker lift trucks, ranging in load capacities from 2,200 pounds to 4,400 pounds.
6. Hand Pallet Trucks
Hand pallet trucks, also known as pallet jacks or pedestrian operated pallet trucks, are manual lift trucks. The truck has two front-facing forks and a rear handle. The operator positions the forks underneath the pallet, and using the hydraulic pump lever, they jack the pallet off the ground, readying it for transport.
As opposed to forklifts, which are for transporting and lifting loads to heights, a hand pallet truck or pallet jack is simply for handling material around the warehouse floor — such as from trailer to storage destination. Hand pallet trucks have a small spatial footprint, which makes them easy to maneuver in tight spaces. Despite being operated entirely manually, a person can easily glide a pallet jack carrying up to 5,000 pounds of goods.
There’s no training or certification required to operate a pallet jack, and it's often the most common lift truck found in any warehouse. It’s affordable, practical and can lift impressively strong loads given its small size. Because there are no motorized parts, hand pallet trucks are considered affordable to purchase, operate and maintain. Hand pallet trucks come in a variety of models with various features. While most are designed for indoor environments with flat, smooth surfaces, there are some built with all-terrain wheels to be used outdoors.
Hand pallet trucks available through Holt of California include the following brands:
7. Tow Trucks
Tow trucks are another type of industrial lift truck typically used in warehouse settings, especially in the automotive sector. Tow trucks are just as they sound — a front towing truck that hitches up to trailers and then tows the trailers around the warehouse. It’s common to see warehouses using tow trucks with multiple trailers towing behind carrying various goods around the facility. Operators drive the tow truck from a front control compartment with a two-way entrance, allowing them to get on and off from either side of the aisle.
Tow trucks are best used in warehouses or facilities that handle itemized goods rather than pallets. This makes them ideal lift and transport trucks for manufacturing facilities as well as retail and e-commerce businesses that carry a range of different consumer goods. Another benefit of having tow trucks is that you can transport multiple loads at once, whereas traditional forklifts limit this efficiency. With long tow trains, you can maximize productivity and not be restricted by the type of load you need to transport.
Holt of California offers Jungheinrich tow trucks as well as tow trucks by Linde.
8. Rough Terrain Forklifts
Different Types Of Lift Trucks
When you're operating lift trucks on challenging, uneven outdoor terrain, you’ll need a forklift with heavy-duty tires designed for rugged conditions. Rough terrain forklifts are diesel-powered lift trucks meant to be operated outdoors on construction sites and in lumber and building supply yards. From wet roads to gravel to slippery mud, rough terrain forklifts are built for uneven surfaces and can easily withstand the elements.
When workers need to lift and move building materials safely, they need the lift power and reassurance of stability on rough terrain. Rough terrain forklift models come in two- and four-wheel drives. While most have straight arms, some have telescoping arms for more accurate and convenient reach and load capacities up to 12,000 pounds. Rough terrain forklifts are classified by OSHA as Class VII, meaning they require additional operator training certification. This is because when the model has a telescoping arm, there is more to know about how to safely operate the lift truck.
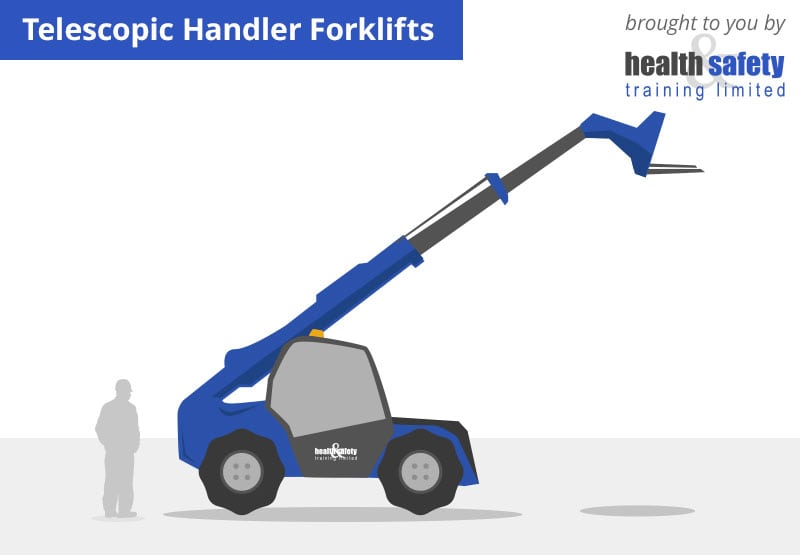
9. Telehandlers
Telehandlers are often considered their own category of equipment, however, they serve the same basic functions as many lift trucks. Telehandlers, or telescopic handlers, are reach forklifts used in agriculture, construction and other industrial capacities. They’re generally built on rugged tires that are ideal for outdoor environments with uneven terrain. The telescoping arm means that the mast extends and retracts from itself, giving it additional reach.
Typically considered to be aerial lifts or personnel lifts, telehandlers help workers achieve heights, and their forks can lift and hoist loads up to 12,000 pounds. As such, the telehandler is a versatile lift truck acting as a forklift, crane and work platform hybrid. Telehandlers also typically have reach capacities greater than forklifts, with some models reaching over 50 feet. This extensive reach capacity makes telehandlers ideal on construction sites with multi-story buildings.
Unlike other lift trucks, telehandlers have multiple steering options. Operators can change from front-wheel-drive when driving on the road to four-wheel-drive for better maneuverability. Telehandlers also offer crab steering mode, allowing the operator to shift loads sideways away from walls or declines.
Find Your Next Forklift at Holt of California
With such a range of different types of forklifts, it can be difficult to know which type you need for your application. From narrow aisle forklifts designed for indoor use to industrial forklifts that can withstand rugged outdoor conditions, there are various types of forklifts to meet your requirements.
When deciding on the right forklift for your business, contact a Holt of California product specialist to learn more about your capacity, height and power needs. Browse our new or used lift trucks for sale or rent, and contact us today with any questions.
